By Prisync
The world of ecommerce is super dynamic, and in this world, pricing isn’t just about numbers—it’s a strategic move that can make or break businesses. In an era where online shopping has become an integral part of our daily lives, mastering it is more crucial than ever.
The latest statistics show us over 2.14 billion people worldwide are expected to make online purchases in 2024. With such a staggering number of potential customers, the stakes are high, and your pricing strategy holds the key to unlocking success. That’s why I want to talk more about various ecommerce pricing strategies and explore the latest trends to help your business thrive in this competitive digital marketplace.
1. Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing, also known as surge pricing or demand pricing, is a strategic approach where businesses adjust the prices of their products or services based on real-time market demand and various other factors. This agile pricing model allows companies to optimise revenue by charging higher/lower prices during peak demand periods and lower/higher prices during off-peak times.
One notable example is the airline industry, where ticket prices fluctuate based on factors such as the time of booking, day of the week, and season. Ecommerce giants like Amazon also employ dynamic pricing algorithms that consider factors like competitor prices, customer behaviour, and inventory levels to set prices dynamically. The formula for dynamic pricing typically involves a combination of historical data analysis, competitor pricing, and current market demand.

This strategy is not only about maximising profits but also about providing consumers with a more personalised and responsive pricing experience. As businesses embrace data-driven decision-making, dynamic pricing continues to be a powerful tool for staying competitive and adapting to the ever-changing market dynamics.
2. Cost Based Pricing
This method requires the company to calculate the unit cost of each product in its portfolio and set a target profit margin for each one.
Final Price = Cost Price + Profit Margin
Most ecommerce businesses have some costs that are common to them. These costs may vary depending on the nature of the business. Some of these costs may include operational expenses, shipping, returns and refunds, used apps, and marketing and advertising costs.
Note: Many ecommerce companies overlook unit costs and cost-cutting strategies. Don’t be one of them!
In any pricing strategy, it is essential to calculate the “costs”, whether it’s a cost-based pricing strategy or not. Plus, when you decide on your profit margin, which is a crucial part of your formula, you can take into account competitor prices and your consumers’ willingness to pay.
3. Bundle Pricing
Bundle pricing is a common pricing strategy that involves offering multiple products or services together as a package at a discounted rate compared to purchasing each item separately. This strategy entices customers by providing added value and encourages them to make a larger purchase. Some brands prefer to offer bundles before purchasing starts; some do it in the baskets just before the last step – the buy button.
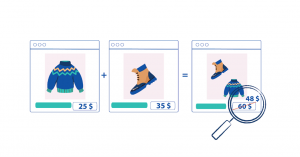
Statistics show that businesses implementing bundle pricing often experience increased sales and higher average transaction values. For instance, tech companies frequently offer software suites that include various applications at a lower combined price than purchasing each program individually. The appeal of bundle pricing lies in its ability to cater to diverse customer needs and preferences while creating a perception of cost savings.
The formula for bundle pricing considers the individual prices of items, the cost of the bundle, and the perceived value to the customer. This strategy not only boosts revenue but also helps companies clear out excess inventory and promote complementary products.
4. Anchor Pricing
This strategy is often used with discounts or promotions to make the discounted price seem more appealing. Statistics indicate that anchor pricing can effectively shape consumer perceptions and drive purchasing decisions.
An example of anchor pricing is commonly found in the retail sector, where a product is initially priced higher than its perceived value, and then promotional discounts or limited-time offers are introduced to create a sense of urgency and value for the consumer.

The formula for anchor pricing considers the psychological impact of the initial high price on consumer perceptions and the strategic placement of discounts or promotions to encourage sales.
While the initial anchor price may not result in high sales, it serves as a reference point for customers, making subsequent discounted prices appear more attractive.
Note: If your anchor price is unrealistic, it can erode trust in your brand and loyalty. To build trust, you can base discounts on a competitive and realistic level.
5. Loss Leader Pricing
A strategy where a company offers a product or service at a price lower than its cost to attract customers and stimulate additional sales of more profitable items. Statistics reveal that loss leader pricing can be a powerful tool for retailers, driving customer traffic and fostering loyalty.
A classic example is the grocery industry, where supermarkets often sell certain items at a loss to entice shoppers into their stores. Once inside, customers are likely to purchase other, higher-margin products, offsetting the loss on the initial discounted item.
The formula for loss leader pricing involves careful analysis of the profit margins on accompanying products and the expected increase in overall sales volume. While the initial product may be sold at a loss, the ultimate goal is to generate a net profit through the sale of complementary or supplementary items.
This strategy is not only about attracting new customers but also about retaining them through a combination of competitive pricing and a diverse product offering. Despite its effectiveness, implementing loss leader pricing requires a strategic approach to ensure long-term profitability and customer satisfaction.
6. Price Skimming
Price skimming is a strategic pricing approach where a company initially sets a high price for a new product or service and gradually lowers it over time. This method is often employed to capitalise on the willingness of early adopters to pay a premium for innovative or exclusive offerings, like the first example that comes to mind: Apple.
Statistics indicate that price skimming can be particularly effective in industries with high levels of innovation, such as consumer electronics.
The formula for price skimming involves carefully considering production costs, market demand, and the perceived value of the product. This strategy allows companies to maximise revenue during the initial product launch and capture different segments of the market as the price decreases over time.
While price skimming may pose challenges in the face of competitive pricing pressures, it remains a valuable tactic for companies aiming to recover development costs quickly and establish a premium brand image in the market.
Create your own unique strategy
We are looking for the “best” pricing strategy, right? However, the best one depends on your business whether its type, size, market, and target. Your own strategy can be a mixed pricing strategy, also known as a hybrid pricing strategy. This is where you combine elements of various pricing strategies to create a customised approach that suits the unique needs and goals of your business.
Statistics show that businesses implementing a mixed pricing strategy can adapt to diverse market conditions and customer preferences effectively. The formula for a mixed pricing strategy requires a comprehensive understanding of the company’s product portfolio, target audience, and competitive landscape. You can take a positioning of each product or service, ultimately contributing to a more resilient and adaptive pricing strategy.
Published 22/02/2024


